Integration with Finance and Operations - From Basics (Part 1)
Introduction
Finance and Operations provides two major ways to interact with tables (or data entities) for external system using APIs; namely Custom Services and Data Entities.
Data entities in D365 Finance and Operations simplify data management by grouping data from multiple tables.
They make it easier to import, export, and integrate data with other systems.
Custom services in D365 Finance and Operations allow developers to create web services for specific business needs.
They enable external systems to interact with D365 F&O by exposing custom logic and operations.
This helps in integrating and automating processes with other applications.
| Feature | Data Entities | Custom Services |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Simplify data management tasks like import, export, and integration. | Expose custom business logic and operations as web services. |
| Functionality | Provide structured access to data from multiple tables in a unified format. | Allow external systems to perform actions or retrieve data via API calls. |
| Usage | Used for bulk data operations, data migration, and integration with external systems. | Used for real-time integration, extending functionality, and custom business process automation. |
| Typical Use Cases | Data import/export, data synchronization, and data migration. | Integrating with external applications, custom business processes, and real-time data access. |
| Data Handling | Focuses on data in bulk. | Focuses on specific operations or business logic. |
Pre-requisites
- A Finance and Operations Environment
- Postman connected to FnO Enviroment (If you want to do this follow the blog here)
References
Data Entities Overview - Finance and Operations
Build and consume data entities - Finance and Operations
Exposing an X++ class as a Data Contract
Configuration
Here, to understand creation of APIs in either cases, we'll expose the same table using both Data Entities and Custom Services.
Data Entity:
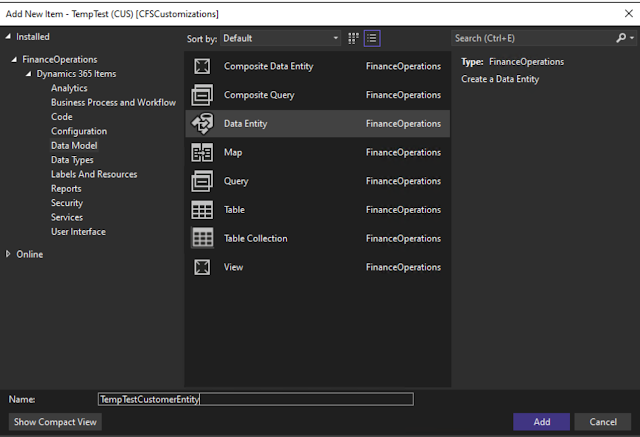
Click on Finance and Operations > Dynamic 365 Items > Data Model and then select "Data Entity"
Select the table that you want to expose in the "Primary Data Source" field, appropirate "Entity Category", "Public Entity Name" and "Public Entity Set Name" (which is what the endpoint will be), and the Staging Table name.
Select the necessary fields from the primary data source.
You can add related tables by clicking on the small arrow next to the table name, which displays the list of all associated tables.
If you want to add new data sources then you can right click on the Primary Data Source's "Data Sources" tab and add new data source.
You can drag fields from any of the data sources into the "Fields" section of the data entity to make them available on the API.
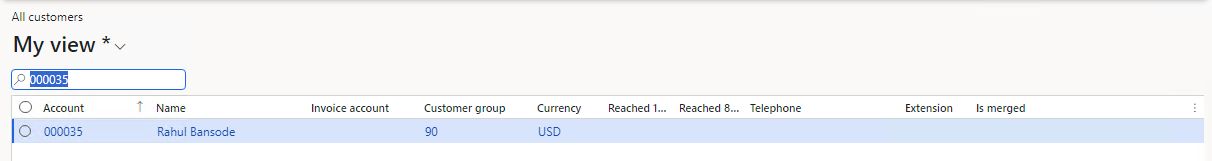
Now, if I need to create a "Customer" record then I can simply pass the same keys into a "POST" request.
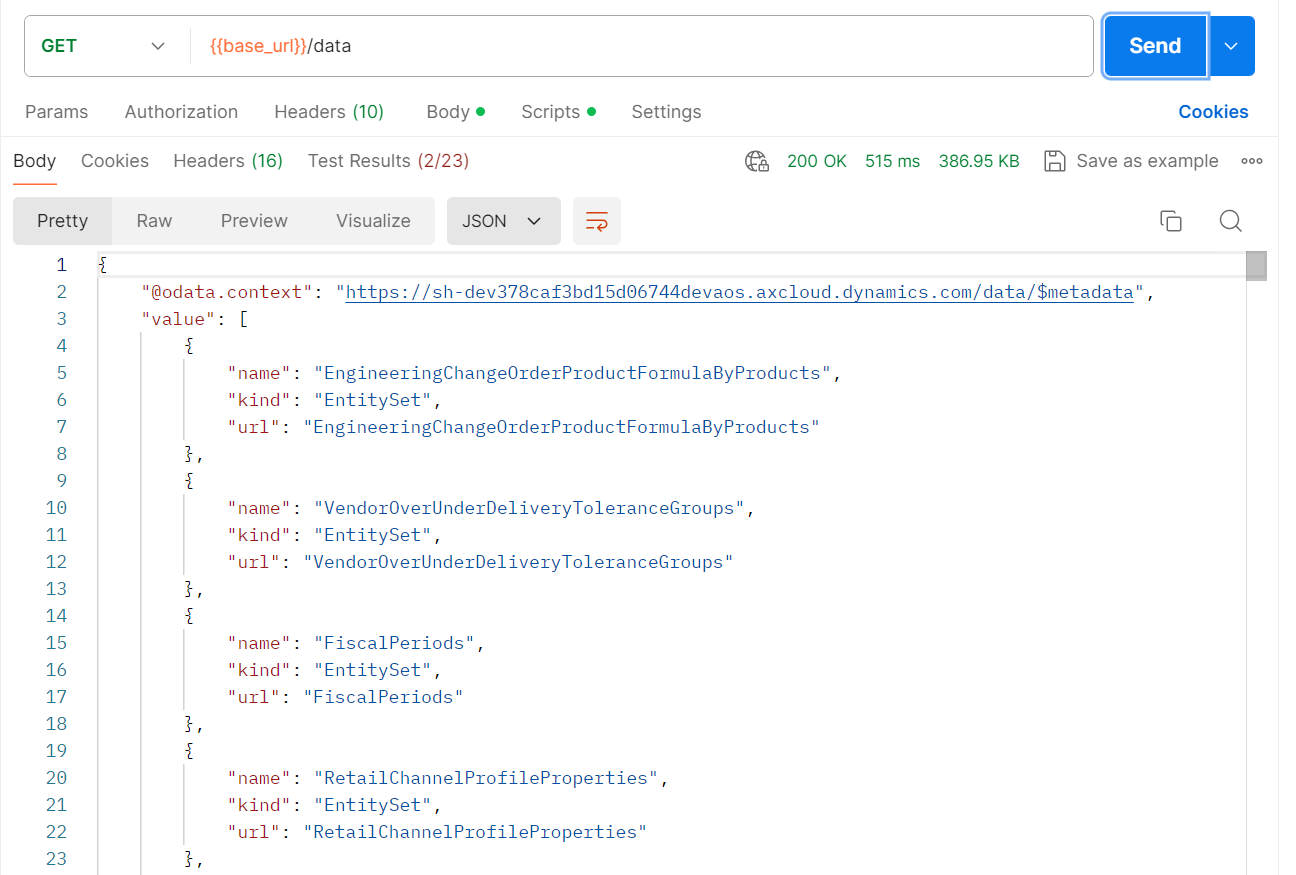
{{base_url}}/data/TestCustomers(dataAreaId='<Company Name>',CustomerId='<Customer Id>')














Comments
Post a Comment